Today Function in Excel
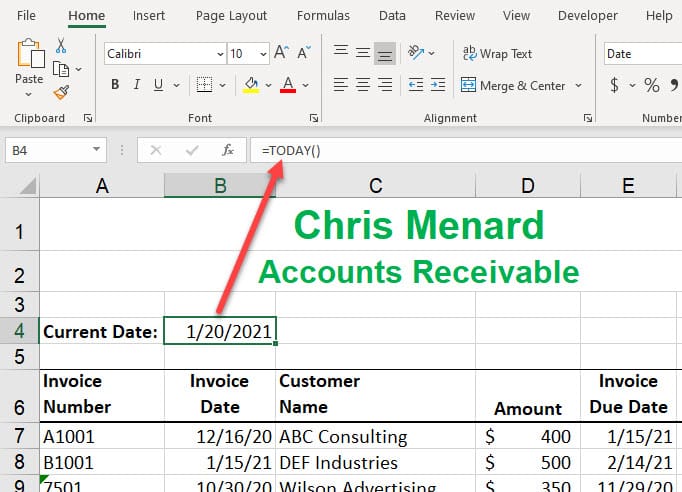
The TODAY function returns the current date. The TODAY function is updated continuously when a worksheet is opened. For example: if you use the TODAY function in cell B1, it will show today's date. Assume that today is 12/21/2021. Tomorrow, it will have the correct date of 12/22/2021.
This video will use the TODAY function with an accounting exercise and an HR exercise. I'll also demonstrate Averageif, Countif, and other functions I use with the Today function.
YouTube Video on the TODAY function
TODAY function in Excel - current date continuously updated - YouTube
Arguments for TODAY function
The TODAY function takes no arguments. **=TODAY()** Notice there is nothing between the parentheses. There are other functions with no arguments. Another popular date and time function is the NOW function. =NOW() which returns the date and time is continuously updated.
Functions with one argument
Some functions use one argument, or where one input is needed. Examples of functions using one argument include Sum, Max, Min, Median, and Average.
Examples of functions with _one_ argument
- =Sum(B2:B12)
- =Average(B2:B12)
- =Median(B2:B12)
- =Max(B2:B12)
Functions with multiple arguments
Some functions have multiple arguments where multiple input is needed. You get a new argument when you add a comma in the function. Excel functions that require multiple arguments.
Examples of functions with multiple arguments
- =COUNTIF(B2:B15,"GA") - Finds people that live in GA in states are listed in column B.
- =LARGE(C2:C15,2) - Finds the 2nd largest number
- =LARGE(C2:C15,3) - Finds the 3rd largest number
- =SMALL(C2:C15,2) - Finds the 2nd smallest number
Related articles
- Three tips for getting started with Excel Charts
Charts in Microsoft Excel are easy. This short video shows three tips for creating charts. I'll cover two keyboard shortcuts for making charts, using Recommend Charts, and creating charts using Quick Analysis. - Tax Brackets Explained using Excel's XLOOKUP function
Tax brackets show you the tax rate you will pay on each portion of your income. There are seven tax brackets. The United States has a progressive tax system based on your Taxable income, not Gross income or Net Income. Your income is taxed at different rates with a progressive tax system. - Covert date to fiscal quarter in Excel
In Excel, to calculate the fiscal quarter that starts with a month other than January, use the CHOOSE function. We will look at fiscal years starting in July, October, and then April in this exercise.
Functions used in video
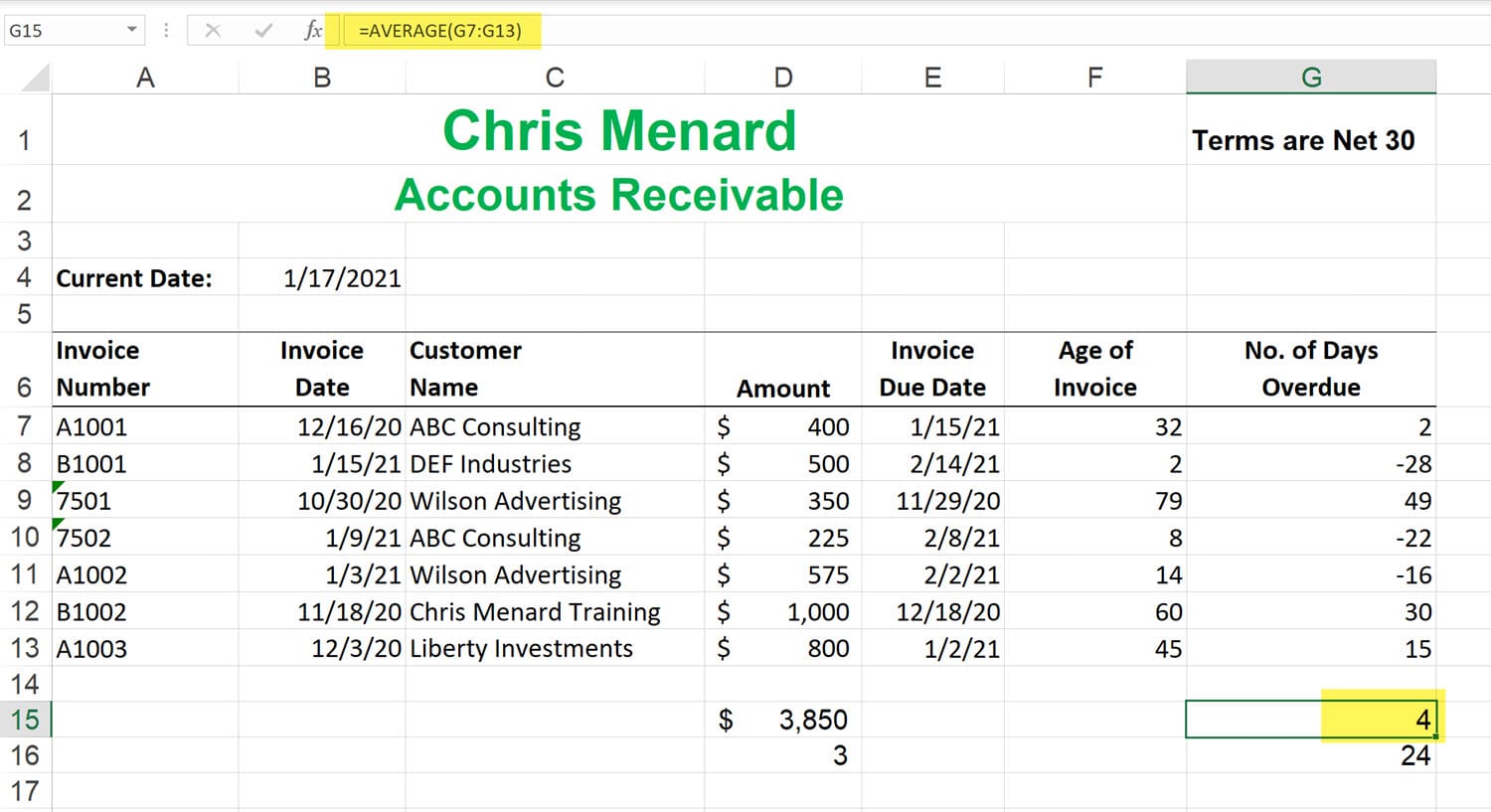
Average Function
Returns the average (arithmetic mean) of the arguments. For example, if the range A1:A20 contains numbers, the formula =AVERAGE(A1:A20) returns the average of those numbers.
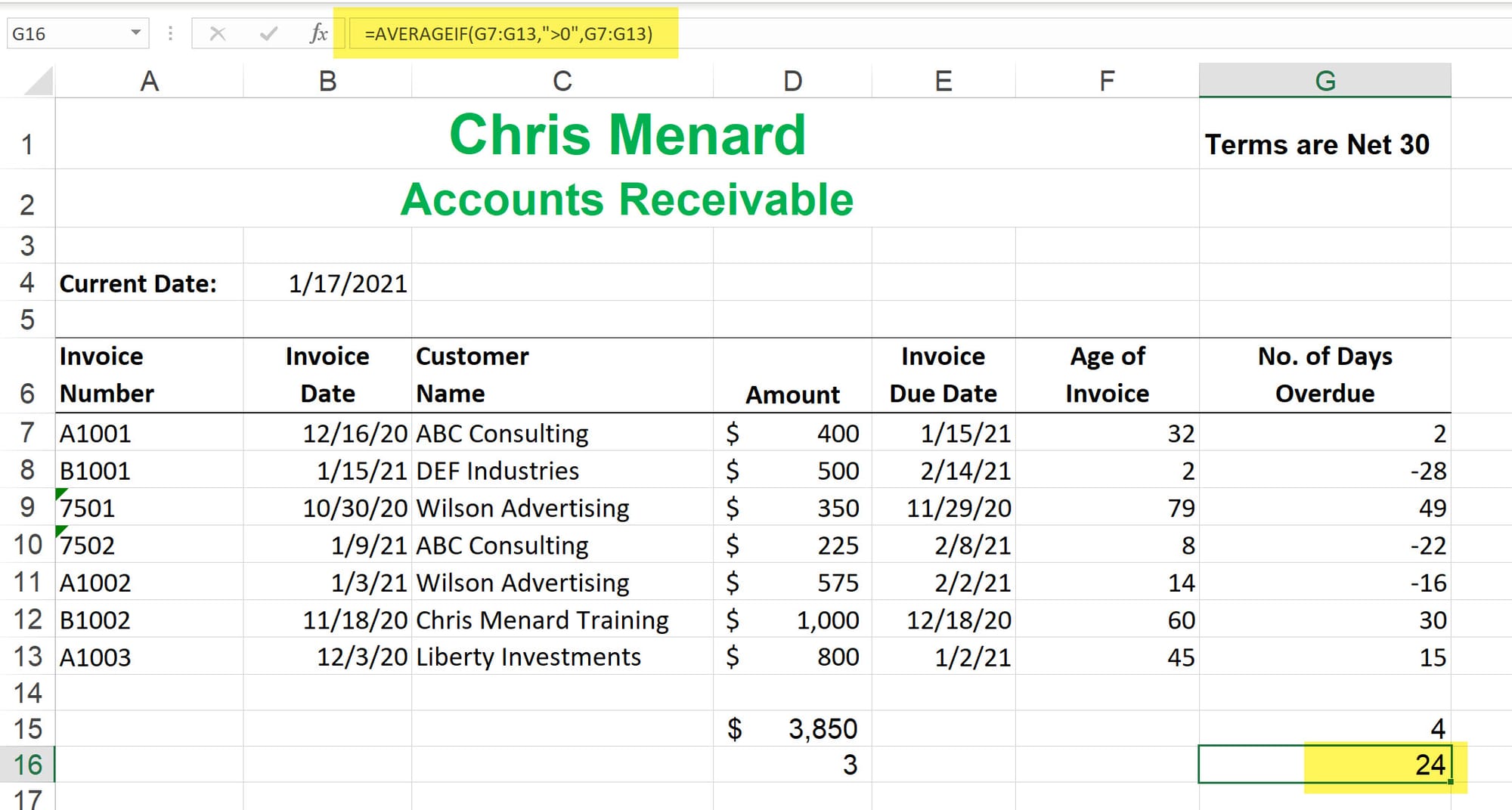
Averageif Function
Returns the average (arithmetic mean) of all the cells in a range that meet a given criteria.
Countif
Use COUNTIF, one of the statistical functions, to count the number of cells that meet a criterion; for example, to count the number of times a particular city appears in a customer list.
DateDif
Calculates the number of days, months, or years between two dates.





