TOROW Function in Excel: Efficiently Organize Your Data

Excel's TOROW function is a powerful tool for data organization, allowing users to convert vertical data into a single horizontal row. This function is particularly useful when you need to reshape your data for analysis or presentation purposes. In this blog post, we'll explore how to use the TOROW function effectively, including its basic usage and advanced features.
YouTube Video: TOROW Function in Excel
Mastering the TOROW Function in Excel - YouTube
Basic Syntax of TOROW
The basic syntax of the TOROW function is:
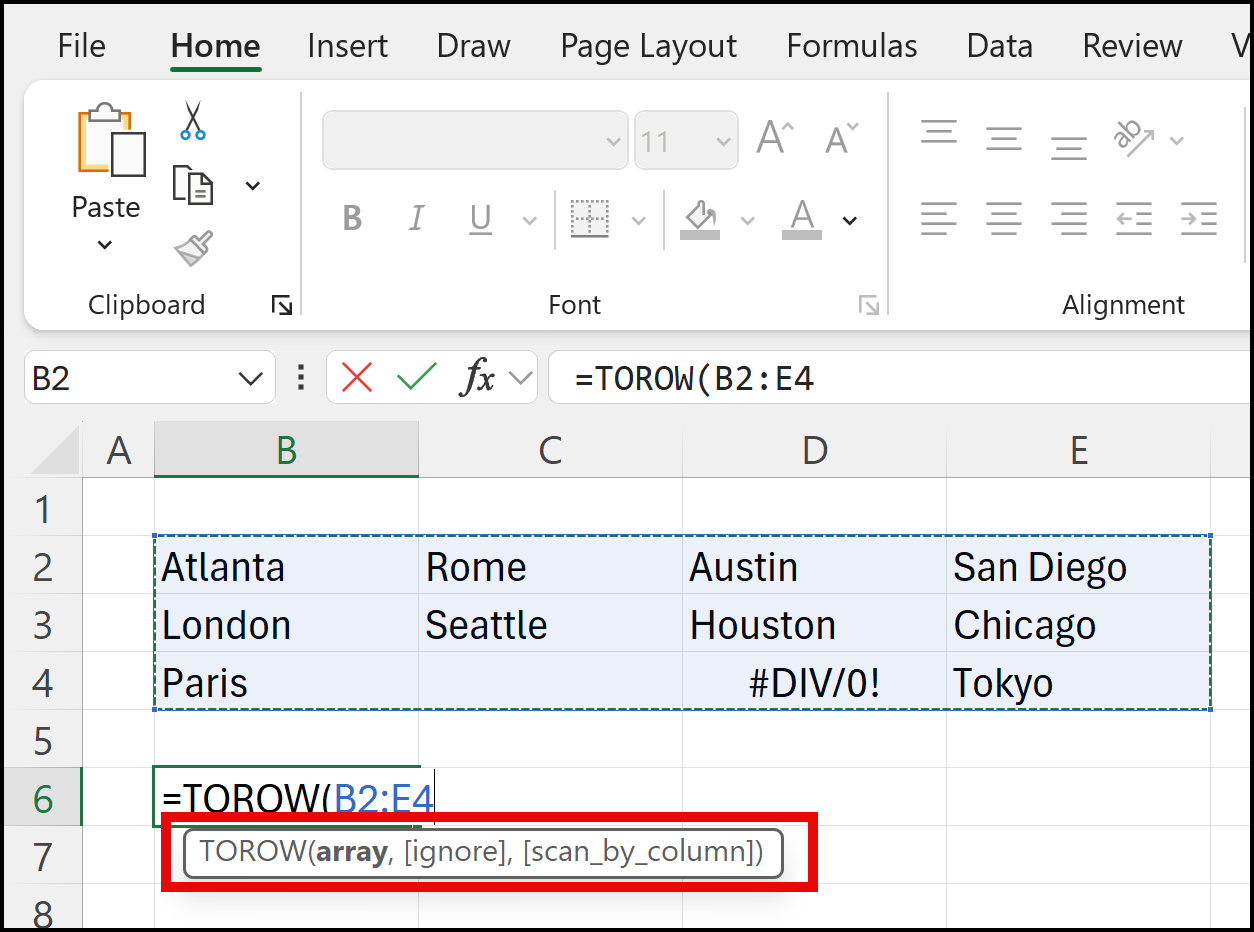
=TOROW(array, [ignore_empty], [scan_by_column])
- array: This is the range of cells you want to convert into a single row.
- ignore_empty: An optional argument that determines whether to ignore empty cells (TRUE) or include them (FALSE). The default is FALSE.
- scan_by_column: An optional argument that specifies whether to scan the data by column (TRUE) or by row (FALSE). The default is FALSE.
Practical Application of TOROW
Let's walk through a practical example to see how TOROW works in action.
Basic Usage of TOROW
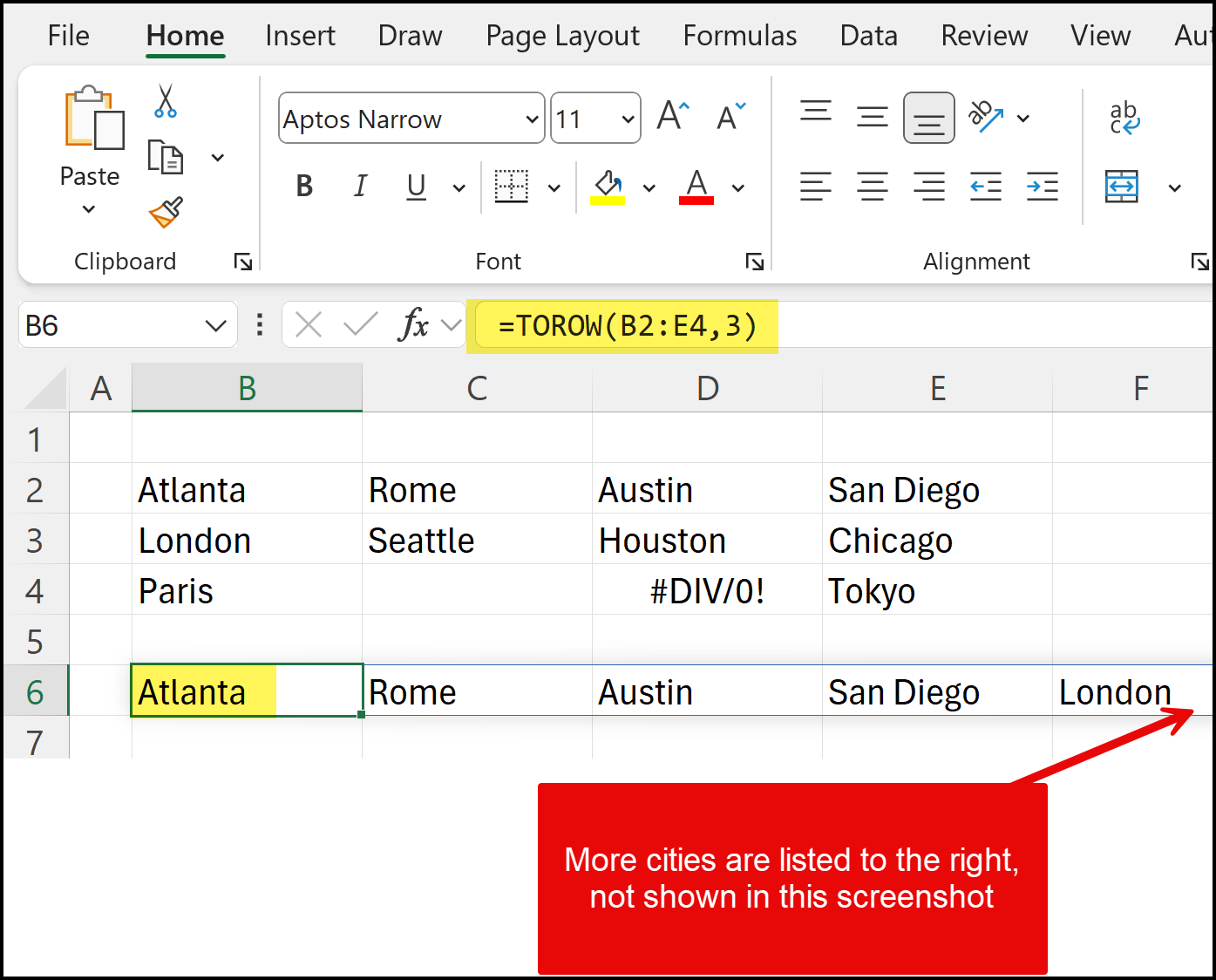
Imagine you have a list of cities displayed from left to right in cells A1:D1: Atlanta, Rome, Austin, San Diego.
To use TOROW, you would enter the following formula in cell B6:
=TOROW(A1:D1)
This formula will take the contents of cells A1:D1 and display them in a single row starting from cell B6.
Handling Blanks and Errors
The TOROW function can also handle blank cells and errors. By default, it includes these in the output. However, you can modify this behavior using the optional arguments.
For example, to ignore blank cells:
=TOROW(A1:D1, 3, TRUE)
This formula will exclude any empty cells from the final output.
Benefits of Using TOROW in Excel
The TOROW function offers several advantages for Excel users:
- Data Consolidation: Quickly combine data from multiple cells into a single row. - Flexibility: Works with both horizontal and vertical data arrangements. - Error Handling: Option to include or exclude blank cells and errors. - Efficiency: Saves time compared to manual data rearrangement.





